Hey there, tech enthusiasts! If you're diving into the world of remote IoT and Raspberry Pi, you're definitely in the right place. Today, we’re going to explore the best ways to set up your Raspberry Pi for remote IoT operations behind a router. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, this guide will give you the tools and knowledge to take your IoT projects to the next level. So, grab your favorite beverage, and let’s get started!
Remote IoT with Raspberry Pi has become a game-changer for both personal and professional projects. Imagine controlling your home appliances, monitoring environmental conditions, or even managing industrial equipment from anywhere in the world. It’s not just about convenience; it’s about creating smarter, more connected systems that enhance our daily lives.
However, setting up a Raspberry Pi behind a router can be tricky if you don’t have the right guidance. That’s why we’ve put together this comprehensive guide to help you navigate through the process. From understanding the basics to advanced configurations, we’ve got you covered.
Read also:Shalom Harlow A Rising Star In The Spotlight
Why RemoteIoT with Raspberry Pi is a Big Deal
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s talk about why remote IoT using Raspberry Pi is such a big deal. The Raspberry Pi is not just a tiny computer; it’s a powerful tool that can be used for a wide range of applications. From smart home automation to data collection and analysis, the possibilities are endless.
Advantages of Using Raspberry Pi for Remote IoT
Here are some of the key advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Raspberry Pi is affordable, making it an excellent choice for hobbyists and small-scale projects.
- Versatile: With a wide range of accessories and software support, Raspberry Pi can be customized to fit almost any IoT application.
- Community Support: A vast community of developers and enthusiasts means you’ll never run out of resources and help.
- Energy Efficient: Raspberry Pi consumes minimal power, making it ideal for long-term deployments.
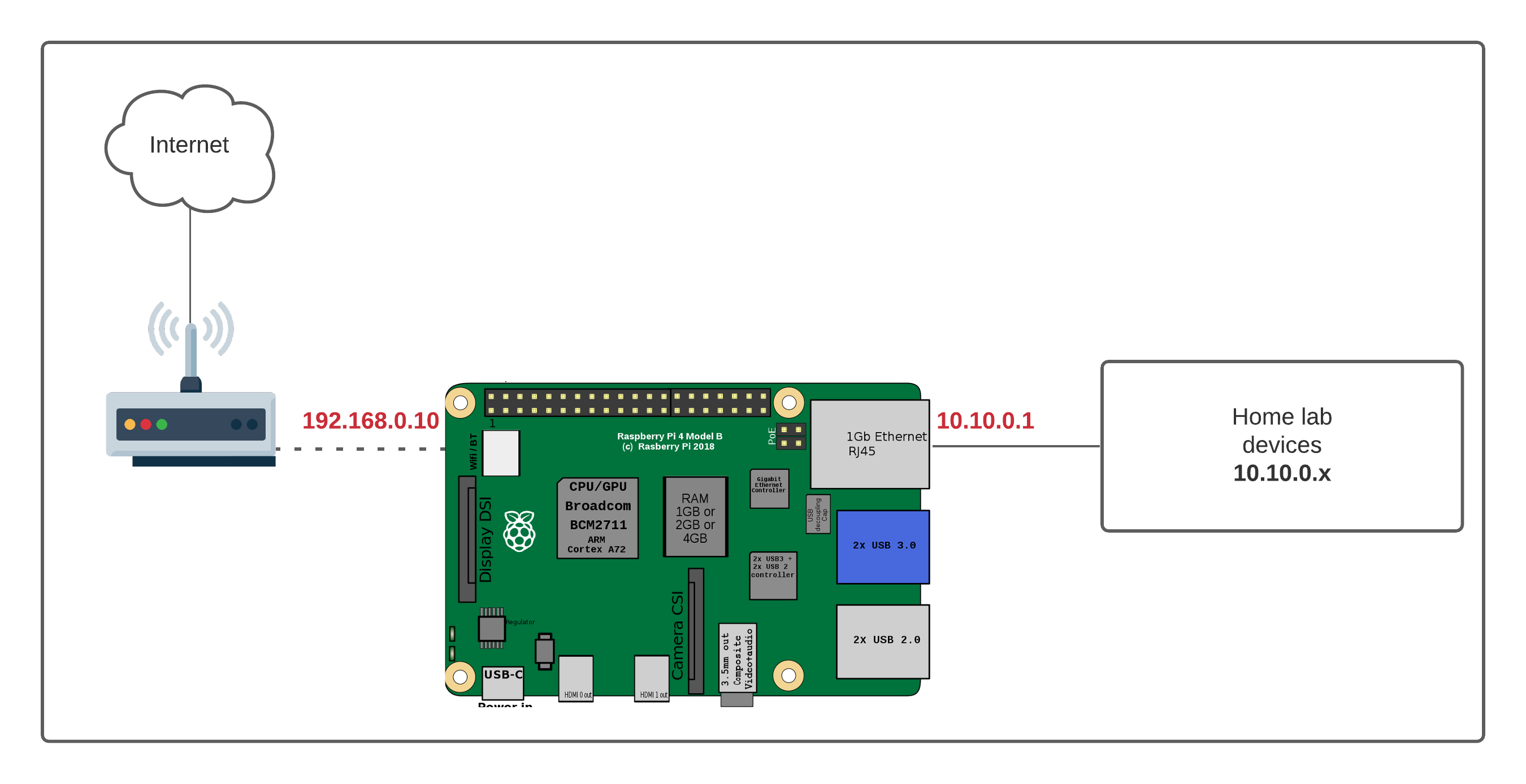
Understanding the Basics of Router Configuration
Setting up your Raspberry Pi behind a router requires a basic understanding of networking concepts. Don’t worry if you’re new to this; we’ll break it down step by step.
Key Networking Terms You Need to Know
Here are some essential networking terms:
- IP Address: A unique identifier assigned to each device on a network.
- Port Forwarding: A technique used to allow external devices to access devices within a private network.
- DDNS (Dynamic DNS): A service that maps a domain name to a changing IP address.
- Firmware: Software embedded in hardware devices like routers to manage their functionality.
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote IoT
Now that you understand the basics, let’s move on to the actual setup process. This section will walk you through the steps to configure your Raspberry Pi for remote IoT operations.
Step 1: Install the Operating System
The first step is to install an operating system on your Raspberry Pi. For remote IoT, we recommend using Raspberry Pi OS or Ubuntu Server. Both are reliable and have excellent support for IoT applications.
Read also:Did Patrick Swayze Have Kids Unveiling The Truth About His Family Life
Step 2: Configure Network Settings
Once the OS is installed, configure the network settings to ensure your Raspberry Pi can connect to the internet. This includes setting up a static IP address and enabling SSH (Secure Shell) for remote access.
Step 3: Set Up Port Forwarding
To allow external devices to access your Raspberry Pi, you’ll need to set up port forwarding on your router. This involves forwarding specific ports to the IP address of your Raspberry Pi.
Step 4: Use DDNS for Easy Access
DDNS simplifies the process of accessing your Raspberry Pi from the internet by providing a consistent domain name. Services like No-IP or duckdns.org offer free DDNS solutions that work great with Raspberry Pi.
Best Practices for Secure Remote IoT
Security is paramount when it comes to remote IoT. Here are some best practices to keep your setup safe:
- Change the default SSH port to something less common.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Regularly update your Raspberry Pi and router firmware.
Advanced Configurations for Enhanced Functionality
Once you’ve got the basics down, you can explore advanced configurations to enhance the functionality of your remote IoT setup.
Automating Tasks with Cron Jobs
Cron jobs allow you to automate repetitive tasks on your Raspberry Pi. Whether it’s running a script at specific intervals or backing up data, cron jobs can save you a lot of time and effort.
Monitoring and Logging
Implementing monitoring and logging solutions can help you keep track of your Raspberry Pi’s performance and troubleshoot issues more effectively. Tools like Logwatch and Grafana are great options for this purpose.
Real-World Applications of RemoteIoT with Raspberry Pi
Let’s take a look at some real-world applications of remote IoT using Raspberry Pi:
Smart Home Automation
Control lights, thermostats, and security systems from anywhere in the world. With Raspberry Pi, you can create a fully automated smart home that adapts to your lifestyle.
Environmental Monitoring
Monitor temperature, humidity, and air quality in real-time. This is particularly useful for agriculture, greenhouses, and industrial settings where environmental conditions play a crucial role.
Industrial IoT
Use Raspberry Pi to monitor and control industrial equipment remotely. This can lead to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved safety.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with the best setup, issues can arise. Here are some common problems and how to fix them:
Connection Issues
If you’re having trouble connecting to your Raspberry Pi remotely, check the following:
- Ensure port forwarding is correctly configured.
- Verify that the DDNS service is working properly.
- Check the firewall settings on your router.
Performance Problems
If your Raspberry Pi is running slowly, try the following:
- Reduce the number of background processes.
- Upgrade the SD card to a faster model.
- Optimize your scripts and applications for better performance.
Resources and Further Reading
Here are some resources to help you dive deeper into remote IoT with Raspberry Pi:
Conclusion
That’s a wrap, folks! We’ve covered everything from the basics of remote IoT with Raspberry Pi to advanced configurations and real-world applications. Remember, the key to success is understanding the fundamentals and building on them step by step.
Now it’s your turn! Take what you’ve learned and start experimenting with your own remote IoT projects. Don’t forget to share your experiences in the comments below and check out our other articles for more tech tips and tricks.
Stay connected, stay curious, and keep building!
Daftar Isi
- Why RemoteIoT with Raspberry Pi is a Big Deal
- Advantages of Using Raspberry Pi for Remote IoT
- Understanding the Basics of Router Configuration
- Key Networking Terms You Need to Know
- Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote IoT
- Step 1: Install the Operating System
- Step 2: Configure Network Settings
- Step 3: Set Up Port Forwarding
- Step 4: Use DDNS for Easy Access
- Best Practices for Secure Remote IoT
- Advanced Configurations for Enhanced Functionality
- Automating Tasks with Cron Jobs
- Monitoring and Logging
- Real-World Applications of RemoteIoT with Raspberry Pi
- Smart Home Automation
- Environmental Monitoring
- Industrial IoT
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Connection Issues
- Performance Problems
- Resources and Further Reading
- Conclusion